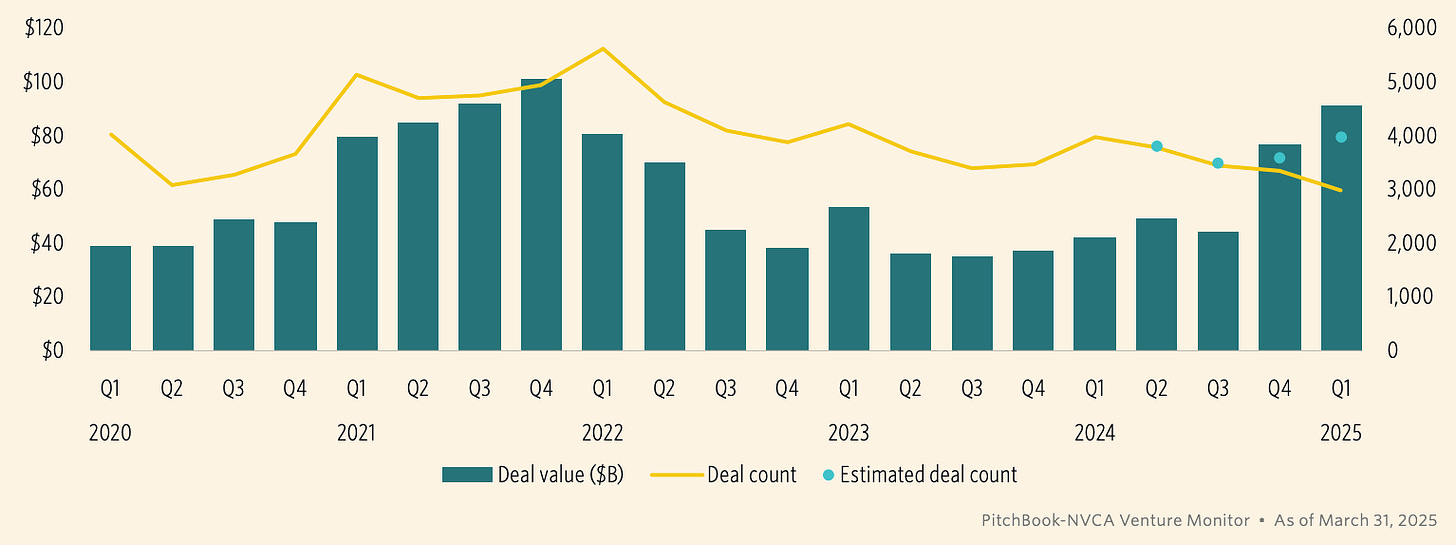
Total U.S. VC deal value surged to $91.5B, marking an 18.5% QoQ increase—the highest since Q1 2022—but the headline is misleading. Ten mega-deals (including OpenAI’s landmark $40B round) accounted for 61.2% of all capital invested, with the remainder of the market remaining subdued. Excluding OpenAI, the next nine largest transactions still made up 27% of total VC dollars, underlining a sustained investor flight to late-stage and AI-centric companies.
Deal count stood at 3,990, up nearly 11% from Q4 2024, but essentially flat YoY compared to Q1 2024. Notably, deals below $5M now comprise just 36% of activity, down from 42.9% in 2023, the lowest share in over a decade. The median pre-money valuation for late-stage VC hit $299M, with venture growth rounds averaging the same—levels not seen since the 2021 bull cycle. Meanwhile, pre-seed and seed rounds showed limited growth in both valuation and activity, pointing to continued early-stage investor hesitance amid uncertain macro conditions.
Artificial Intelligence remains the singular bright spot in an otherwise tepid market. AI and ML-related startups captured a stunning 71.1% of total U.S. VC capital in Q1, a sharp rise from 46.8% in 2024 and just 33.2% in 2023. Beyond OpenAI, Anthropic raised $4.5B across two rounds, Infinite Reality secured $3B, and Groq raised $1.5B, confirming that large-cap tech incumbents are not pulling back from AI despite macro uncertainty and potential tariff-driven chip supply shocks. However, any disruptions in AI hardware costs due to escalating trade policies could dampen this momentum moving forward.
At the same time, exit activity remains historically muted. Only 12 companies completed IPOs in Q1, and nearly 76% of M&A exits occurred before companies reached Series B—highlighting a low-return environment that limits distribution to LPs. While CoreWeave’s IPO and the acquisition of Wiz generated the highest exit value since Q4 2021, these outliers mask the underlying drought. According to J.P. Morgan’s commentary, IPO timelines are stretching, and exit readiness activities are increasing—but they’re not yet materializing into actual listings. Secondary markets, however, are heating up—over 50% of late-stage rounds in the past six months included secondary components, up from 20–30% historically, offering partial liquidity as traditional exit windows remain shut.
Fundraising, too, reflects investor caution. Q1 2025 marked the lowest quarterly fundraising pace in over a decade. Investors are rotating capital into proven winners, with little appetite for new or unproven managers. First-time financings dropped both QoQ and YoY, with just $3.8B deployed across 892 deals, underscoring growing selectivity among LPs. This risk-off sentiment is compounded by macro and policy turbulence—new tariffs, public market volatility, and delayed Fed rate cuts are discouraging new commitments. In parallel, corporate venture capital (CVC) participation dropped below 23% of total deal count, even as dollar participation hit a record 61.1%, largely driven by AI-led mega-deals.
Crypto Deal Volume Hits Post-2022 High
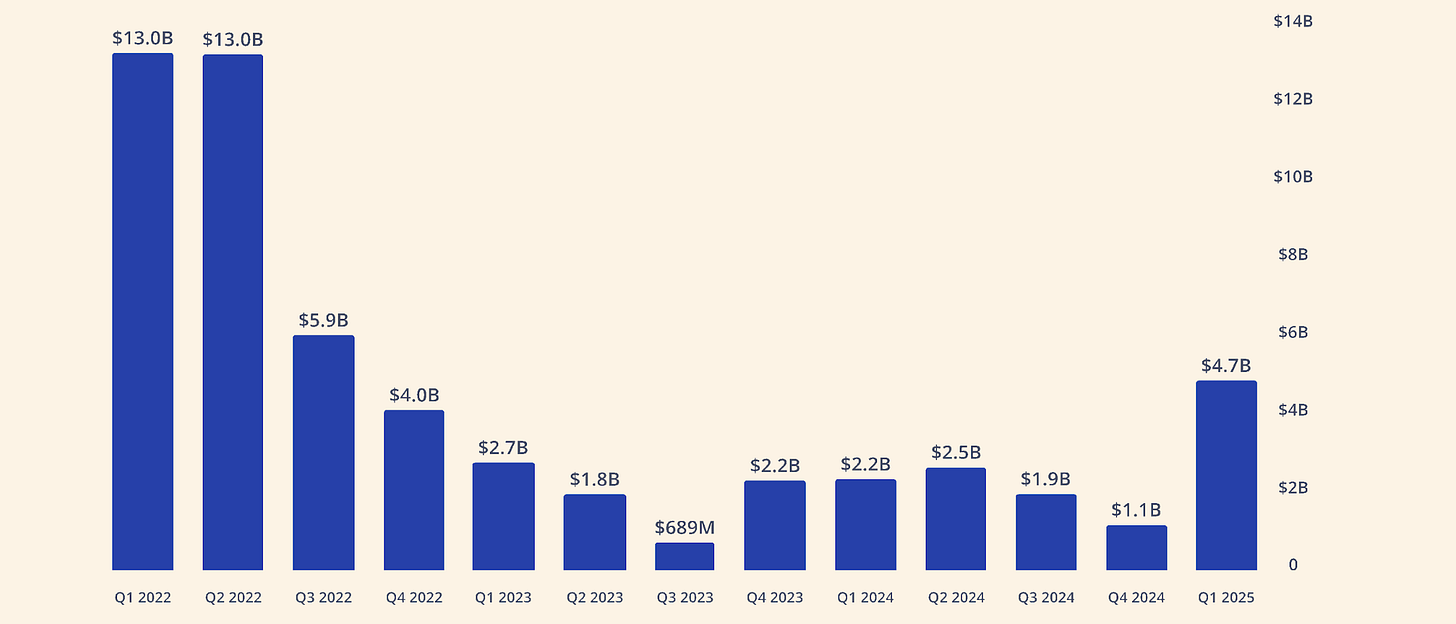
In Q1 alone, global crypto VC investments reached $4.8 billion, the highest quarterly total since late 2022. This single quarter was 60% of all VC capital deployed in 2024, signaling renewed investor appetite despite a cautious macro backdrop. Notably, the number of deals dipped slightly even as total capital rose, indicating larger round sizes on average. Early-stage activity remained robust (Seed rounds were the majority of deals), but 12 large-scale deals over $50M closed in Q1, reflecting greater willingness to back more mature projects.
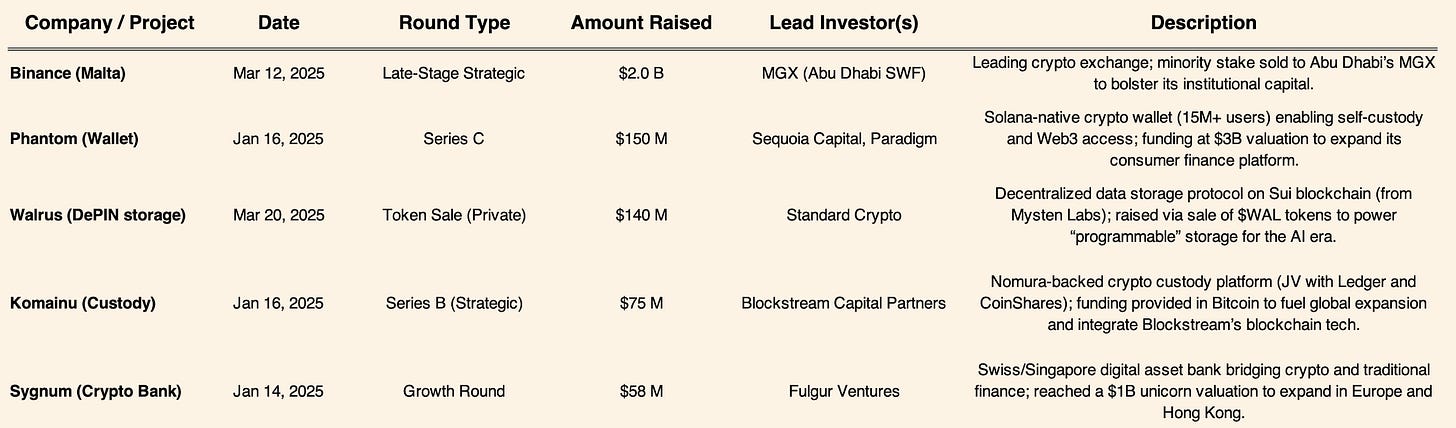
Venture investments in Q1 clustered around CeFi infrastructure, blockchain services, and DePIN (decentralized physical infrastructure networks). For example, CeFi plays like Binance and Phantom attracted large rounds to scale exchanges and wallet platforms. DePIN startups gained traction with Walrus’s hefty $140M raise for decentralized storage. Investors also showed growing appetite in AI x Crypto and Real-World Asset (RWA) sectors. While dedicated AI-crypto startup funding was modest, traditional crypto firms are integrating AI capabilities (e.g. Chainalysis’s acquisition of Alterya for fraud detection – see M&A) to enhance their services. The RWA tokenization narrative continued to build: crypto bank Sygnum’s funding underscored interest in platforms bridging real assets with blockchain. Overall, Q1 venture data suggests the early stages of a new cycle – one focused on projects with pragmatic utility and institutional appeal, from blockchain infrastructure (e.g. custody, compliance) to novel Web3 use-cases like DePIN and RWA integration.
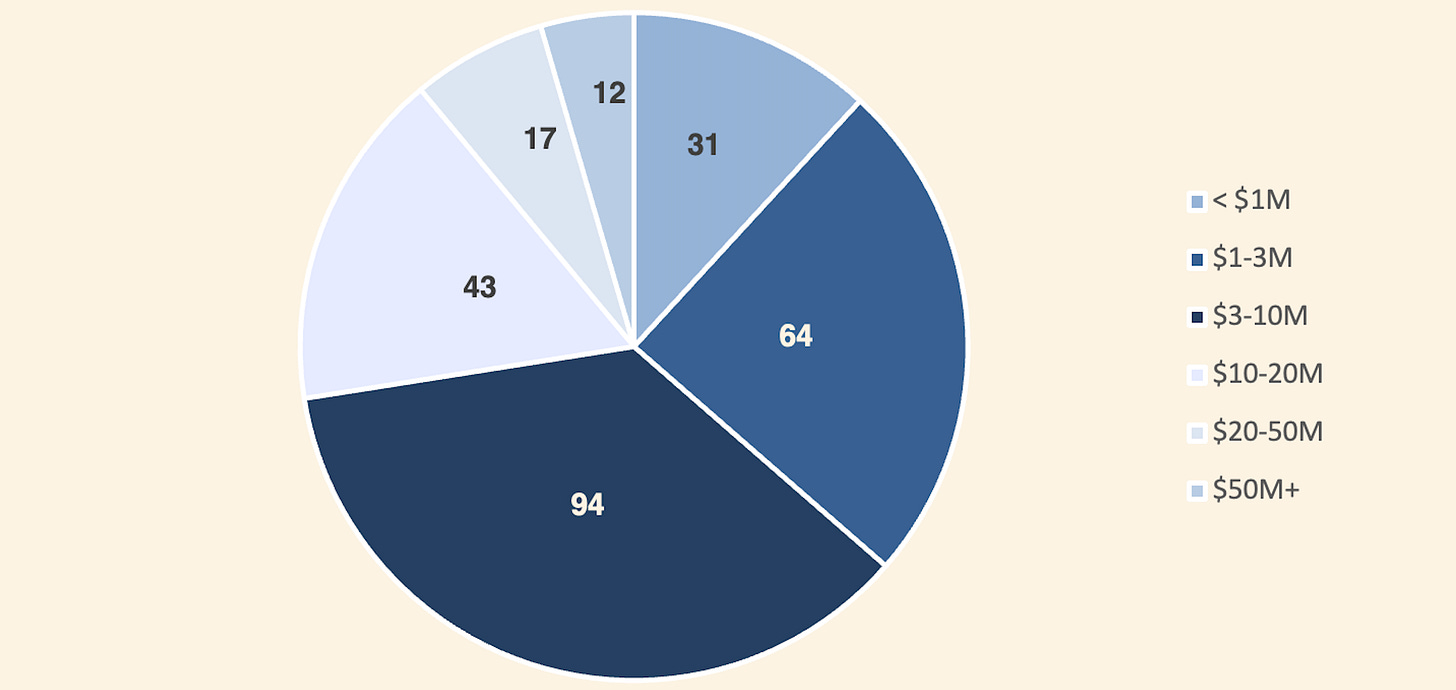
In Q1 2025, nearly two-thirds of crypto fundraising rounds were under $10 million, highlighting ongoing support for early-stage innovation. However, the emergence of 12 mega-deals exceeding $50 million reflects growing investor confidence in mature, high-impact projects with proven traction and institutional backing.
M&A and Private Equity Transactions
Consolidation accelerated as both crypto-native companies and traditional firms executed major mergers, acquisitions, and strategic investments in early 2025. More than two dozen crypto/Web3 acquisitions were announced by mid-March, indicating that buyers are taking advantage of improved market sentiment and regulatory clarity. Key M&A and private equity deals in Q1 2025 included:
Kraken acquires NinjaTrader (March 2025, $1.5 B): U.S.-based crypto exchange Kraken agreed to buy NinjaTrader, a leading retail futures trading platform, for $1.5 billion. The deal (expected to close in H1 2025) gives Kraken a foothold in U.S. regulated futures and multi-asset trading. It reflects deepening ties between crypto companies and traditional finance, as crypto players expand into stocks and derivatives. An Oppenheimer analyst noted this is a “crypto-native acquiring a TradFi” platform – a landmark $1B+ deal highlighting the convergence of the two sectors. Kraken plans to operate NinjaTrader as a standalone brand, leveraging its ~2 million user base and licenses to integrate crypto futures offerings.
MoonPay acquires Helio (Jan 2025, $175 M): Crypto payments firm MoonPay purchased Helio, a Solana-based crypto payments processor, for a reported $175 million. Helio enables merchants to accept digital currencies (USDC, SOL, ETH, etc.) and has processed over $1.5B in transactions with 6,000+ merchants. MoonPay’s CEO called the acquisition “an important step in advancing our vision for the future of payments”, as it bolsters MoonPay’s infrastructure for crypto commerce and marketplaces. The deal gives MoonPay a robust on-chain payments gateway (integrated with Discord, Shopify, etc.) to complement its fiat-to-crypto onramp business, indicating consolidation in the crypto payments and merchant services segment.
Chainalysis acquires Alterya (Jan 2025, $150 M): Blockchain analytics company Chainalysis bought Alterya, an Israeli AI-powered fraud detection startup, in a deal valued around $150 million. Alterya uses artificial intelligence and vast scam databases to block fraudulent transactions in real-time. By combining Alterya’s AI agent approach (stopping scammers mid-transfer) with its own on-chain data, Chainalysis aims to “sniff out yet more scammers” and broaden its compliance solutions beyond crypto into traditional finance. This acquisition illustrates a trend of crypto firms acquiring fintech/AI startups to strengthen risk management. (Notably, Alterya had only raised ~$6M prior, meaning a high-multiple exit, indicative of strong strategic value.)
Coinbase acquires BUX Europe (Q1 2025, amount not disclosed): In a regulatory-driven play, Coinbase quietly acquired the Cyprus arm of Dutch brokerage Bux, securing a MiFID II investment firm license in the EU. The deal (announced in October 2024 and completed by early 2025) gives Coinbase a regulated entity to offer crypto derivatives and CFDs across European markets. While small in dollar terms, this highlights how TradFi licensing needs are spurring M&A – established crypto companies are buying traditional financial entities to expedite compliance and market access in jurisdictions like the EU.
Other notable deals straddling crypto and traditional sectors included SoftBank’s $50M investment into bitcoin miner Cipher Mining (providing growth capital to crypto infrastructure), and Abu Dhabi’s $2B investment in Binance (discussed in VC section), which was effectively a private equity stake by a sovereign-backed fund. Together, these moves underscore a pattern of consolidation: well-capitalized crypto companies are acquiring capabilities (trading platforms, payments tech, AI tools), while traditional tech/finance players are entering the crypto space via acquisitions. This is fueled by a more favorable regulatory outlook – U.S. policy shifts under a pro-crypto administration have eased fears and “pulled in” big buyers. Industry figures expect continued crypto-TradFi convergence, as large institutions ask “What’s our strategy? Why aren’t we doing this?” and seek to catch up. Indeed, 2025 could see Web3 startups “get bought” en masse, turning the long-awaited promise of exits into reality.
Stripe–Bridge and XRP–Hidden Road Deals
Stripe’s $1.1 B Stablecoin Bet – Acquisition of Bridge
Global fintech company Stripe made waves with a late-2024 move that closed in early 2025: it acquired Bridge – a stablecoin infrastructure startup – for a reported $1.1 billion. Bridge, founded in 2022 by former Coinbase executives, is a payments network dubbed the “web3 version of Stripe” because it allows businesses to easily create, store, and transfer stablecoins on multiple blockchains. The deal, announced in October and finalized by January, is Stripe’s largest acquisition ever and one of the largest in crypto M&A history.
We recommend checking out our paper from a few weeks ago that provides a detailed breakdown of Stripe’s acquisition of Bridge: https://insights4vc.substack.com/p/stripes-stablecoin-strategy
Stripe’s purchase of Bridge signals a strong commitment to blockchain-based payments and stablecoins. Stripe had already begun integrating Circle’s USDC and other stablecoins into its platform for global merchants. By buying Bridge, Stripe obtains a turnkey platform for issuing and managing stablecoins, accelerating its crypto capabilities. Stripe processes ~1% of global GDP in payments, so enabling stablecoin transactions could significantly expand its reach. Javelin Strategy’s analysts commented that the deal affirms Stripe’s view that stablecoins will proliferate in use-cases from cross-border payments to digital commerce. In short, the Bridge acquisition gives Stripe both the technology and talent (Bridge’s team of ex-Coinbase engineers) to become a major player in crypto payments, likely integrating stablecoin issuance for Stripe’s millions of business clients. This landmark fintech-crypto deal also delivered a quick win for Bridge’s VC backers (Index Ventures and Haun Ventures reportedly tripled their investment) and set a precedent for fintech incumbents buying crypto startups at unicorn valuations.
Ripple’s $1.25 B Hidden Road Acquisition – “Once-in-a-Lifetime” Deal
In April 2025, Ripple Labs – the company behind the XRP cryptocurrency – announced an agreement to acquire Hidden Road, a multi-asset prime brokerage firm, for $1.25 billion. This is one of the largest acquisitions ever by a crypto company and will make Ripple the first crypto-native firm to own and operate a global prime broker. The deal (revealed April 8, 2025) is expected to close in the coming months pending regulatory approval.
Below is a breakdown of this landmark transaction:
Participants: Acquirer – Ripple Labs, a leading blockchain payments company valued around $15B (as of its last funding) and provider of the XRP Ledger. Target – Hidden Road, a well-established prime brokerage that provides clearing and trading services across foreign exchange, fixed income, swaps, and digital assets for institutions. Hidden Road was founded by CEO Marc Asch and serves over 300 institutional clients, clearing more than $3 trillion annually in volume. Notably, Hidden Road has been a liquidity partner in the crypto markets (it’s described as “crypto-friendly”) and even uses Ripple’s USD stablecoin in its operations.
Deal Structure: The acquisition is an all-cash deal for $1.25B (no stock consideration has been reported). Ripple will use its significant cash reserves – bolstered by past XRP sales – to finance the purchase. The deal will allow Hidden Road to expand exponentially using Ripple's balance sheet. In other words, Ripple is injecting a large amount of risk capital and providing its regulatory licenses to Hidden Road, enabling the prime broker to accelerate growth. Hidden Road’s CEO confirmed that with Ripple’s “new resources, licenses, and added risk capital, this deal will unlock significant growth” and allow them to enter new markets and product lines. Post-acquisition, Hidden Road is expected to continue operating under its current management (Marc Asch will remain at the helm) but with much deeper capitalization. This structure ensures continuity for Hidden Road’s clients while leveraging Ripple’s funding.
Strategic Motivations: For Ripple, this is a bold move to expand from being primarily a cross-border payments and crypto liquidity provider into a full-scale institutional finance player. By owning Hidden Road, Ripple gains a platform to offer prime brokerage services – trading, custody, financing, and clearing – to hedge funds and financial institutions. Ripple’s CEO Brad Garlinghouse called the acquisition a “once-in-a-lifetime opportunity” that gives crypto companies “access to the largest and most trusted traditional markets – and vice versa.” In essence, Ripple aims to bridge the gap between crypto liquidity and traditional asset markets. Hidden Road’s infrastructure and client network bring instant credibility and connectivity to institutional capital markets. This could supercharge XRP’s utility as well: Garlinghouse noted Hidden Road will integrate XRP and the XRP Ledger (XRPL) to expedite trade settlement and enhance efficiency. In fact, Hidden Road plans to migrate its post-trade clearing onto XRPL, showcasing the blockchain’s ability to handle high-volume institutional flows. The deal also enhances Ripple’s stablecoin strategy – Hidden Road already uses Ripple’s USD stablecoin (RLUSD) as collateral across its prime brokerage services. With ownership of Hidden Road, Ripple can push broader adoption of RLUSD and XRP for settlement, potentially making XRP part of the plumbing in traditional markets. For Hidden Road, joining forces with Ripple provides a massive capital infusion and crypto expertise at a time when digital assets are gaining favor. Hidden Road will be able to grow its business faster and scale globally, backed by Ripple’s ~$1B+ war chest. Asch, the CEO, said the Ripple partnership would let Hidden Road “increase capacity, expand into new product lines, and service more markets with institutional-grade reliability.” In short, Hidden Road gets a strong balance sheet and access to Ripple’s blockchain tech, while Ripple inherits a ready-made prime broker to distribute its crypto liquidity.
Public Commentary: The acquisition has been heralded as a defining moment for Ripple and XRP. Analysts note it “cements [Ripple] as the first crypto-native firm to run a global prime brokerage” and could usher in a new chapter for XRP’s role in finance. Ripple’s CEO portrayed the timing as ideal, saying “the U.S. market is effectively open for the first time” now that regulatory overhangs have lifted, enabling deals that address the needs of traditional finance. U.S. regulators, under a more crypto-friendly administration, recently signaled openness to crypto (indeed this was the second $1B+ crypto deal of 2025 after Stripe–Bridge). This supportive climate likely gave Ripple confidence to pursue such a large acquisition. From the Hidden Road side, industry observers highlight that being owned by Ripple (which has deep crypto liquidity and an established network of banks using its RippleNet payments system) could allow Hidden Road to offer unique services – e.g. on-demand crypto liquidity for FX trades, or real-time settlement via blockchain, differentiating it from traditional prime brokers. In the words of one market commentator, the deal “could bring the largest institutional capital and crypto markets together,” potentially accelerating adoption of XRP if Ripple successfully integrates its technology into Hidden Road’s workflows.
Other Mega Deals and Capital Movements (> $100M)
Beyond formal venture rounds and M&A, Q1 2025 saw several mega-sized transactions in the crypto/Web3 arena, including token buybacks, strategic token programs, and unconventional capital transfers:
StepN’s $100M Token Buyback & Burn (March 2025): StepN, the popular “move-to-earn” Web3 fitness app, initiated a community-driven buyback of its governance token GMT. The StepN DAO repurchased 600 million GMT tokens (worth about $100 million), with a proposal to burn (permanently destroy) them pending a user vote. This “Burn GMT” initiative aimed to drastically reduce GMT’s circulating supply, potentially boosting its value for holders. The rationale was to reward the community and shore up the token’s economics: by cutting supply nearly 10%, StepN signaled long-term commitment to token value. Holders were invited to lock tokens and vote on burning the repurchased GMT, in return for rewards (e.g. exclusive NFTs and reward pools). Such a large-scale token buyback is rare in crypto – StepN effectively used $100M of its treasury (accumulated from profits) to invest back in its ecosystem, akin to a public company stock buyback. This move – described as a potential “game-changer” for the GMT token – underscores how some Web3 projects are leveraging treasury funds to manage token supply and incentivize their user base.
Binance’s $2B Funding via Stablecoins (March 2025): As noted earlier, Binance’s $2 billion raise from Abu Dhabi’s MGX was not only the largest venture deal but also featured a unique structure: the investment was transacted entirely in stablecoins. The parties did not disclose which USD-pegged stablecoin was used, but executing a multi-billion-dollar equity investment via crypto stablecoins is unprecedented in scale. This method allowed fast settlement across borders and aligns with Binance’s crypto-centric operations. It illustrates the growing use of crypto assets for corporate finance – a sovereign-backed fund effectively bought a stake in a major company using digital dollars. The deal’s stablecoin structure also points to MGX’s and Binance’s comfort with blockchain-based transactions for serious sums, potentially foreshadowing more large deals being settled on-chain. (Notably, regulators later lauded the transparency of recording such a transaction on a public ledger, even as the specific stablecoin remained private.) This stablecoin-funded equity round highlights creative dealmaking that blends traditional private equity with crypto liquidity.
Bitget–Bybit Emergency Fund Transfer (April 2025, ~$100 M): In a remarkable display of exchange-to-exchange support, crypto exchange Bitget transferred nearly $100 million in ETH to competitor Bybit after Bybit suffered a major security breach. The incident, which occurred in late March, saw Bybit lose a substantial amount of assets to a hack. Bitget’s management chose to temporarily lend support by moving ~$100M of ether to Bybit’s wallets to shore up its reserves. This alliance in crisis – effectively a short-term lifeline – is virtually unheard of among rival exchanges, but it was deemed critical to prevent contagion and maintain confidence in the broader market. Bybit was able to continue operating without solvency issues, and Bitget’s unusual aid was seen as a move to stabilize the industry (and perhaps signal Bitget’s own strength, with PoR >130% throughout the quarter). The transfer was reversed after Bybit raised funds to cover the loss, but it set an example of crypto firms coordinating in emergencies akin to how banks sometimes act in concert during financial crises. Such cooperative behavior, while rare, could become a precedent as the crypto sector matures and recognizes collective resilience is beneficial.
Conclusion
These mega transactions underscore the diverse ways capital is flowing in the crypto/Web3 space beyond straightforward investments. From protocol treasury maneuvers (token buybacks/burns) to novel deal financing (stablecoin payments) and even crisis management solidarity, Q1 2025 demonstrated a maturing ecosystem willing to deploy nine-figure sums strategically. For institutional investors, these developments are notable: they show crypto companies using tools analogous to traditional finance (buybacks, M&A) as well as uniquely crypto-native solutions. The net effect is a more robust, interconnected crypto industry – one where large capital can be mobilized quickly and sometimes collaboratively. Heading further into 2025, analysts expect more such mega deals and innovative structures, as consolidation continues and both crypto incumbents and TradFi entrants leverage significant capital to shape the Web3 landscape.
Sources
Q1 2025 - PitchBook NVCA Venture Monitor:
Risk Disclaimer:
insights4.vc and its newsletter provide research and information for educational purposes only and should not be taken as any form of professional advice. We do not advocate for any investment actions, including buying, selling, or holding digital assets.
The content reflects only the writer's views and not financial advice. Please conduct your own due diligence before engaging with cryptocurrencies, DeFi, NFTs, Web 3 or related technologies, as they carry high risks and values can fluctuate significantly.
Note: This research paper is not sponsored by any of the mentioned companies.



great post